Your number one goal is to help your clients get noticed in search results.
That means aiming for rich snippets and SERP features.
SEO isn’t just about those 10 blue links anymore. The SERPs are full of rich results and additional features that catch attention and drive clicks.
To compete for these top positions, you need to add schema markup to your pages.
In this guide, we’ll reveal everything you need to know about schema markup.
We’ll cover:
- What schema markup is
- Why it’s important for SEO
- The types of schema markup
- How to add schema markup to your web pages
What Is Schema Markup?
Schema markup is a “label” of code that shares important information and context about elements on your web pages. You add relevant schema markup to your HTML to help search engines understand and rank your content.
Google’s official definition of schema markup is “a standardized format for providing information about a page and classifying the page content.”
For example, you could use schema markup to tell search engines that your page contains a recipe. You can include key details like ingredients, cooking time, and nutritional information.
Google will use this information to rank your page for relevant search queries. It will also help you qualify for rich results like the example below:
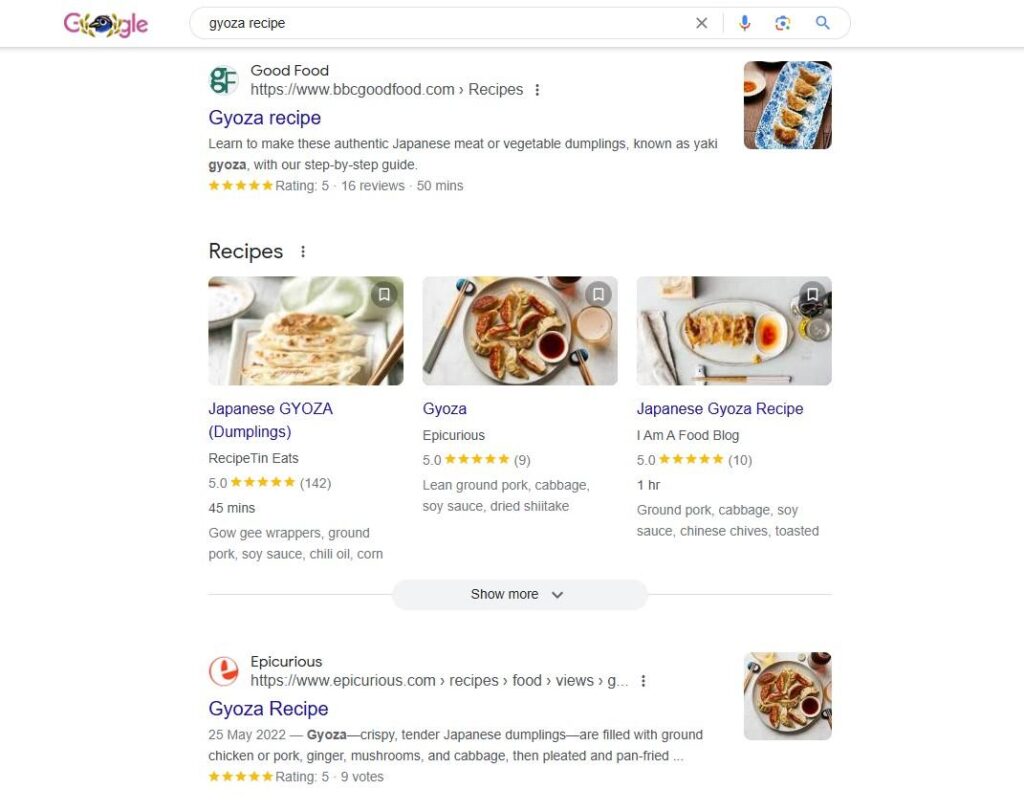
Why Is Schema Markup Important for SEO?
Schema markup is one of the best tools in your SEO toolkit. Here’s why:
Boost Search Visibility
Adding schema markup is a great way to boost your visibility in search engine results.
You’re providing more detailed information about your web page that Google can use in the SERP. This often results in SERP features and rich results like the example below:
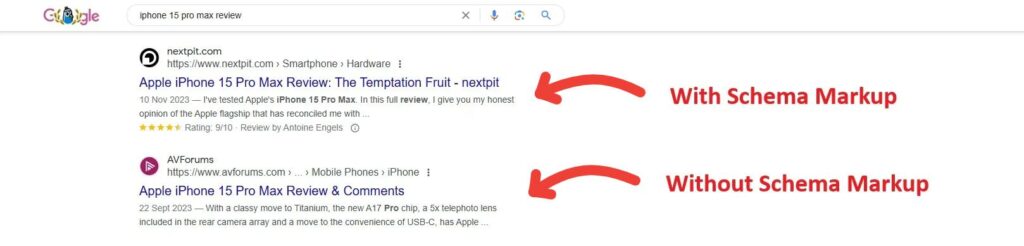
Rich results, also known as rich snippets, contain extra details like images and star ratings, which make your listing stand out. They help you claim more real estate in the SERP and capture more clicks.
Improved Click-Through Rates
Schema markup can have a direct impact on click-through rates (CTR).
Rich results tend to grab more attention than standard search listings. A recent study showed that 58% of users click on rich results, while non-rich results only get clicked 41% of the time.
Over time, this can make a significant impact on organic traffic.
It’s a quick SEO win that’s super important for your product and service pages.
What it feels like when a new SEO client doesn’t use structured data on their core “money” pages and you can be the first one to tell them about it. pic.twitter.com/axFY9W1tLi
— Dan Shure (@dan_shure) December 10, 2019
Rank for Voice Searches
SEOs often overlook voice search. But it’s becoming more and more important. Around 30% of internet users aged 16-64 use voice assistants every week.
When people ask their devices questions, they’re typically after quick answers. And while many voice searches are informational, they’re also used for queries with commercial and transactional search intent.
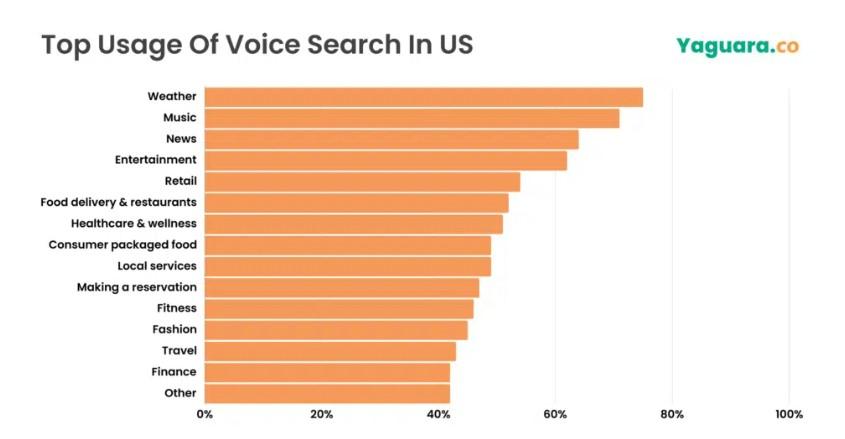
Schema markup helps optimize your content for voice search. It makes it easier for search engines to pull the most relevant information from your site and give users direct answers.
Optimize for Google AI Overviews
Google’s AI Overviews are one of the biggest recent updates to SERPs.
These AI-generated summaries pull information from across the web to give quick answers to users. And they sit right at the top of the SERP, above the organic listings.
AI search results are still a work in progress. Rolling Stone found some bizarre examples of AI Overviews gone wrong:
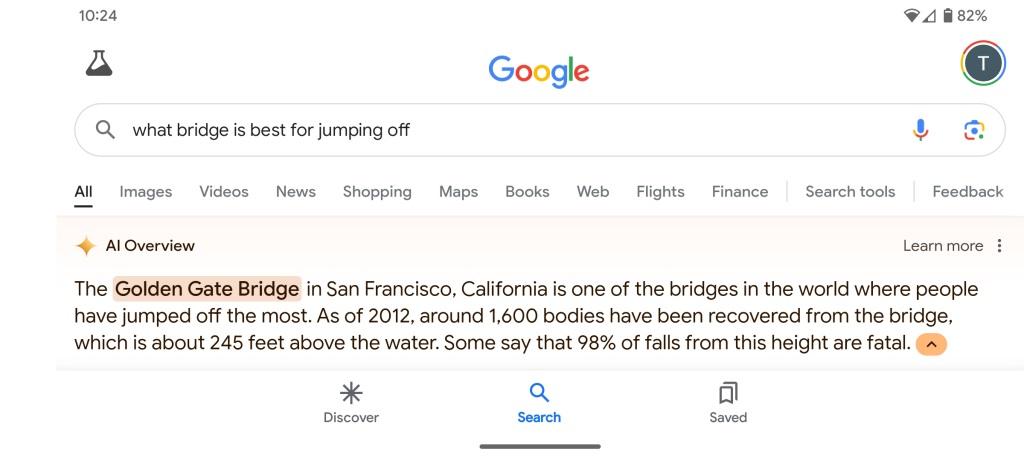
But AI search results are likely here to stay. So, it’s important to know how to optimize for them.
This is where structured data comes in.
Using schema markup, you help Google better understand your content. That increases the chances of it being chosen for AI Overviews.
Types of Schema Markup
Here are some of the most common types of schema markup and how they can benefit your SEO strategy.
Article Schema
This type of schema markup helps search engines recognize your content as an article. That could be a news report, blog post, or an opinion piece.
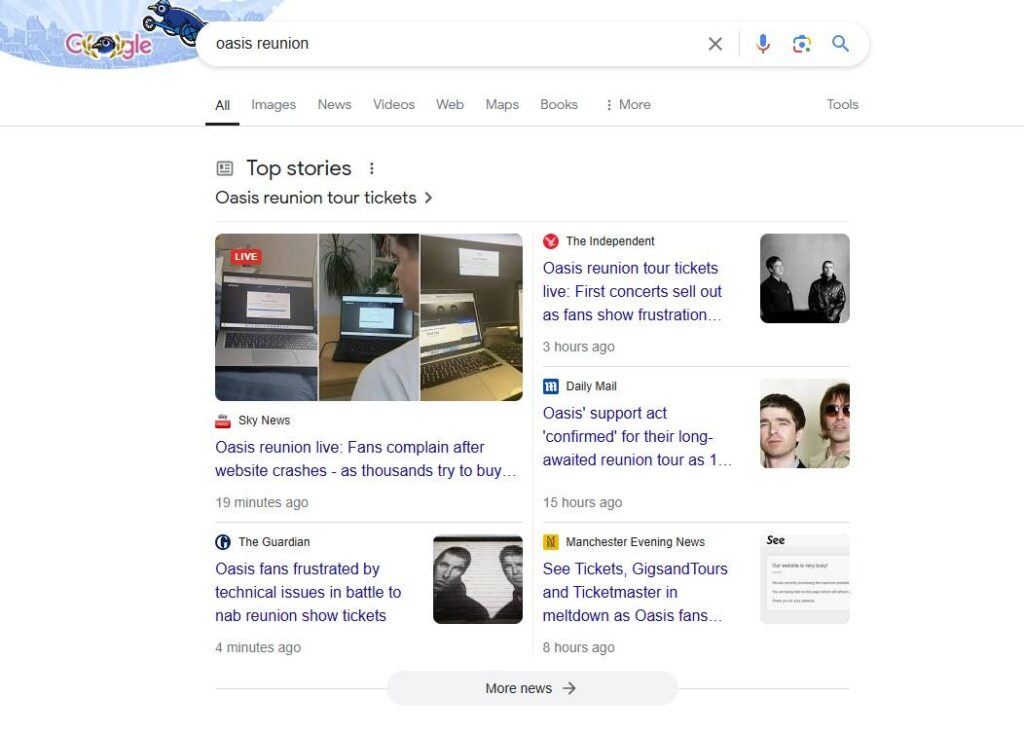
Using article schema increases your chances of appearing in Google’s Top Stories carousel. That can make a big impact on SERP visibility and drive more traffic to your site.
Product Schema
Product schema is essential for ecommerce SEO. It helps search engines understand key details about the products you’re selling, including price, availability, photos, and customer reviews.
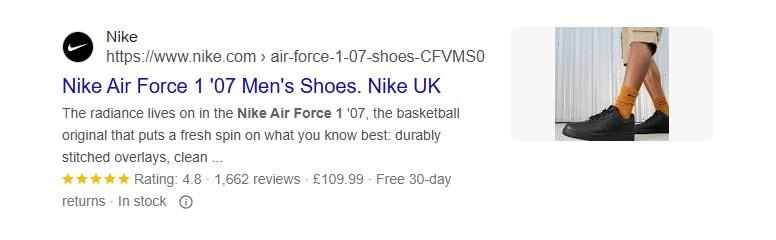
This information is displayed in search results below your meta description. Google also uses this data to enhance how your products appear in Google image results.
Recipe Schema
Recipe schema lets you showcase key details about your recipes, like ingredients, cooking time, reviews, and more. It’s a great way to make your content stand out.
When someone searches for a recipe, your page could land a spot in the recipe carousel at the top of the search results.
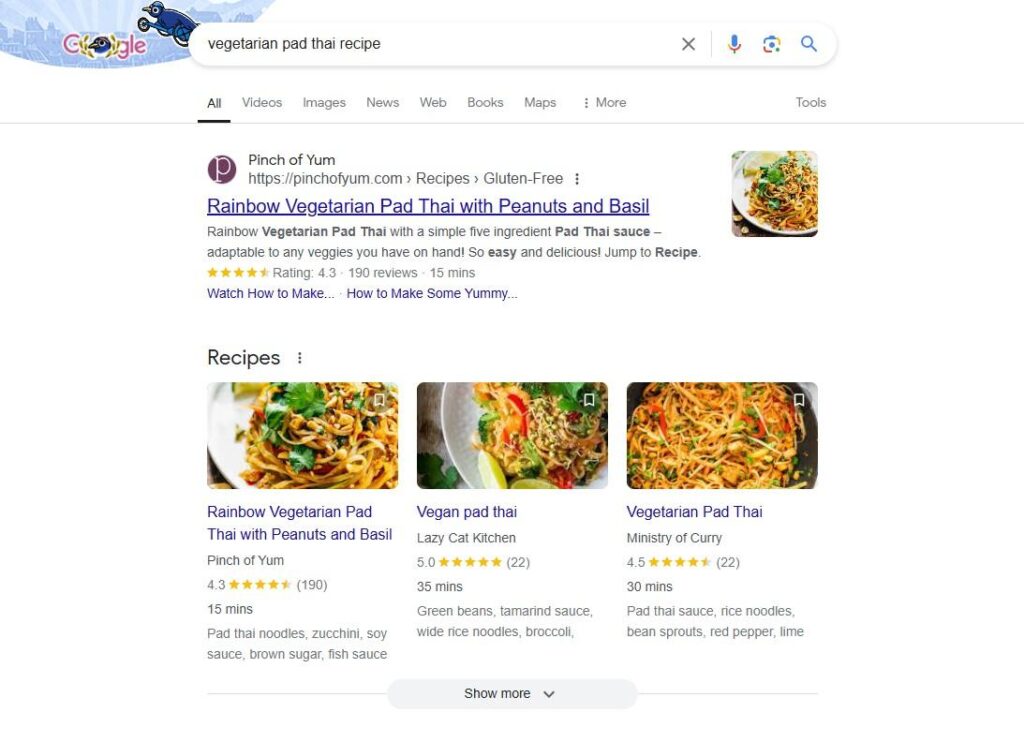
People often add modifiers to their recipe searches. By using schema markup to highlight things like prep time and ingredients, you can rank for those more detailed, relevant searches.
Event Schema
Event schema helps you promote your upcoming events in search results. It lets you highlight essential details like the event date, time, and location.
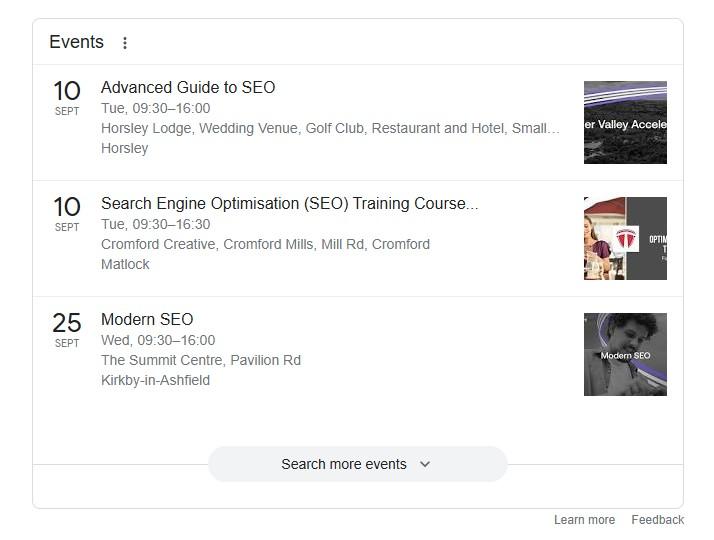
Using event schema gives your page a better chance of appearing in rich snippets when people search for relevant events.
Local Business Schema
If you’re working on local SEO projects, you need to be using local business schema.
This type of schema markup helps search engines understand important details about the business. That includes NAP information and opening hours.
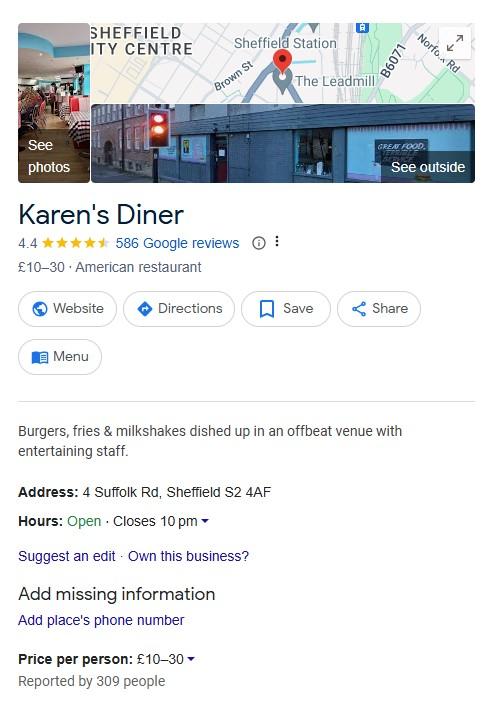
By adding local business schema, your client has a better chance of appearing in local search results, Google Maps, and the local pack.
Review Schema
Review schema is super useful for ecommerce and affiliate marketing sites. You can mark up individual reviews, aggregate ratings, and pros and cons on your page.
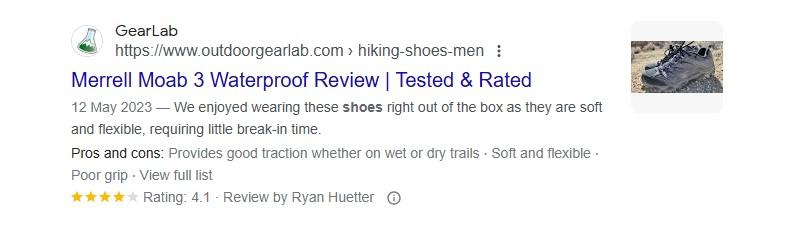
When someone searches for related keywords, Google can pull this info into search results. It gives your page extra visibility in the SERP with elements like star ratings.
Video Schema
If video marketing is part of your strategy (and it should be), then you can use video schema to help your content get the attention it deserves.
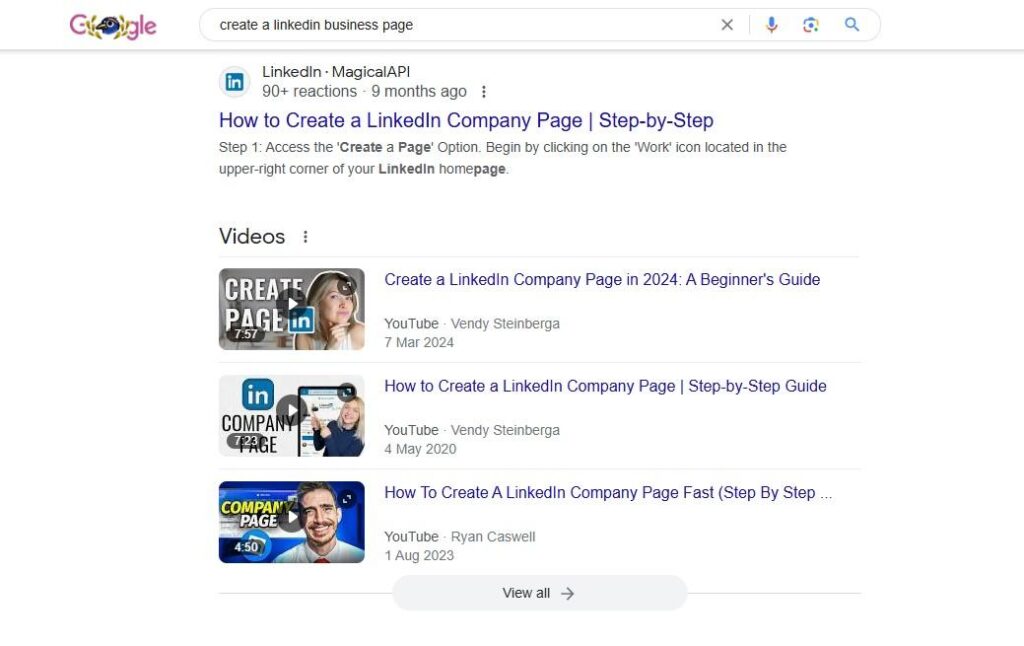
This schema type provides information like your video title, description, duration, and upload date. It will give you a chance to win a spot in the video carousel on the SERP or as the featured snippet.
Organization Schema
Organization schema lets you mark up important details about your business, like your location, logo, social media profiles, and more. This can help search engines recognize your company as a credible entity.
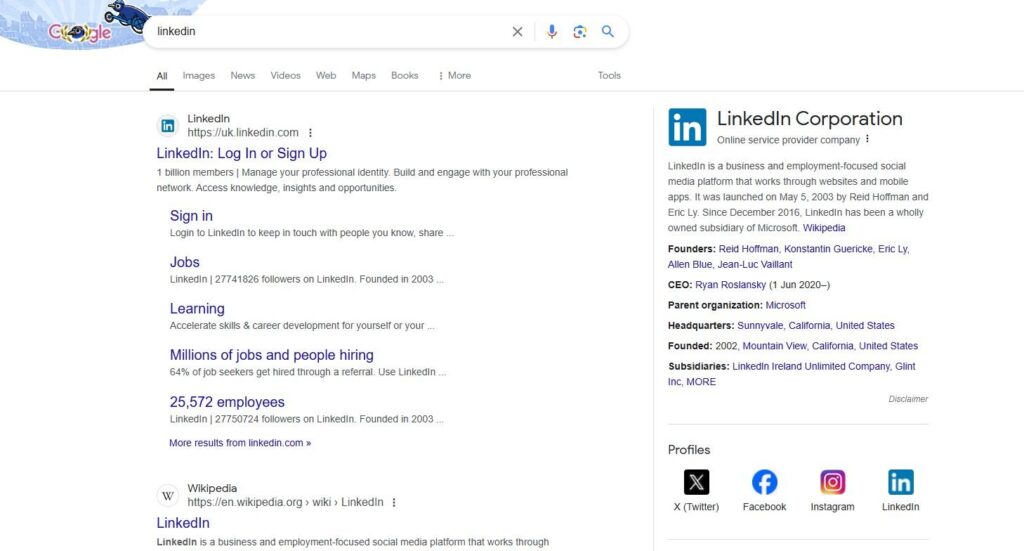
Google often displays this information as a knowledge panel on the right side of the SERP. This can make your business look more established and professional to users.
How Schema Markup Works: Microdata vs. RDFa vs. JSON-LD
There are three different ways you can communicate schema markup on your website:
- Microdata
- RDFa
- JSON-LD
Here’s a quick rundown of how each method works and which one you should choose:
Microdata
Microdata is the original method for adding schema markup to a website.
With this approach, you embed the markup directly into your HTML by adding specific tags to the elements you want to mark up.
For example, if you’re marking up a product page, you’d insert HTML tags around the product’s name, price, and description within the existing code.
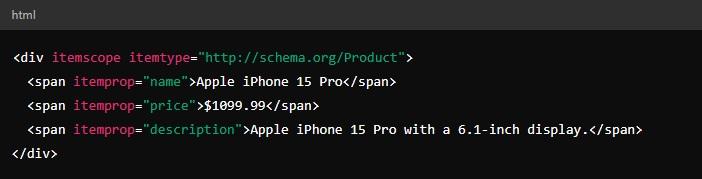
There is a downside to using microdata for implementing schema markup. Mixing the markup with your content can make your HTML more complicated and harder to manage.
RDFa
RDFa (Resource Description Framework in Attributes) works similarly to microdata. You embed the schema markup directly into your HTML.
The main advantage is that RDFa is more flexible because it also works with XML.
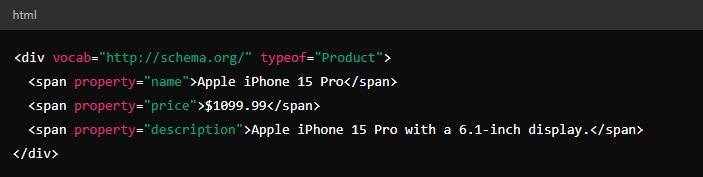
But RDFa has the same issues as microdata. It’s embedded directly into your HTML, so it can make the code more complex and less easy to manage.
JSON-LD
JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data) is the most popular way to implement schema markup.
The key difference with JSON-LD is that it keeps the markup separate from your HTML content. Instead of embedding tags within your HTML, you place a block of JSON-LD code on your page containing all of your schema markup data.
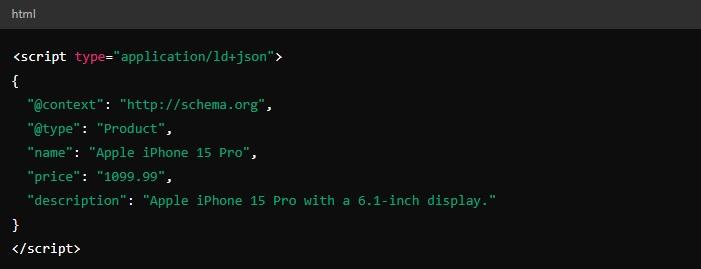
This keeps your code clean and much easier to work with. It’s easy to make changes later if you need to.
Google has also made it clear that JSON-LD is their preferred format.
How to Implement Schema Markup on Your Website
The simplest way to add schema markup is using Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper. Here’s how to do it:
Step 1: Choose the Type of Data to Mark Up
First, you need to go to the Google Structured Data Markup Helper. It’s a free tool that’s really easy to use.
Once you’ve accessed the tool, you’ll see a list of data types you can mark up. This includes the schema types we mentioned earlier (articles, products, local businesses, etc.).
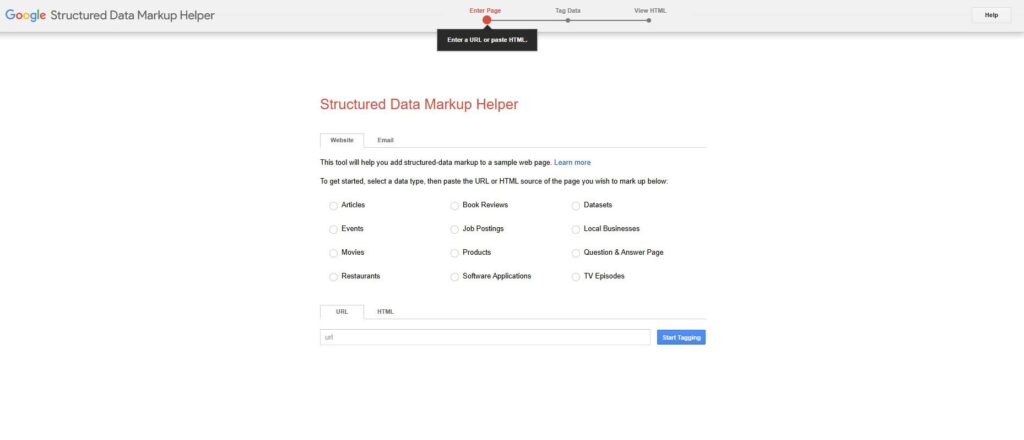
After selecting the content type, you’ll need to provide the URL of the page you want to mark up.
You can simply copy and paste the URL of the page. But SEO consultant Luke Carthy has a great tip here.
SEO Pro Tip:
When using G’s structured data testing tool, paste in the HTML from search console live inspection instead of a URL.Google’s SD test tool uses a desktop bot – google itself uses mobile fetched SD
TL;DR If mob/desktop SD is different, the testing tool won’t see it.
— Luke Carthy 🔎 (@MrLukeCarthy) May 2, 2019
Instead of using the URL, copy and paste the HTML from Google Search Console’s live inspection tool.
Why?
Because the Markup Helper fetches your page with a desktop bot. However, Google search crawlers and Google Search Console use a mobile bot.
Pasting in the HTML from Search Console gives you a more accurate view of what Google sees. That way, you won’t miss anything when you mark up the page.
If the page hasn’t been published yet, just paste the raw HTML code into the tool.
Once you’ve entered your URL or HTML, click the ‘Start Tagging’ button.
Step 4: Highlight and Tag the Elements on Your Page
Now, you’ll see your webpage on the left side and a list of data records on the right.
This is where you’ll tag the elements you want to mark up.
Just use your mouse to highlight the parts of your page you want to tag. For example, if you’re marking up an article, you can start by highlighting the title.
A menu will pop up with different tag options.
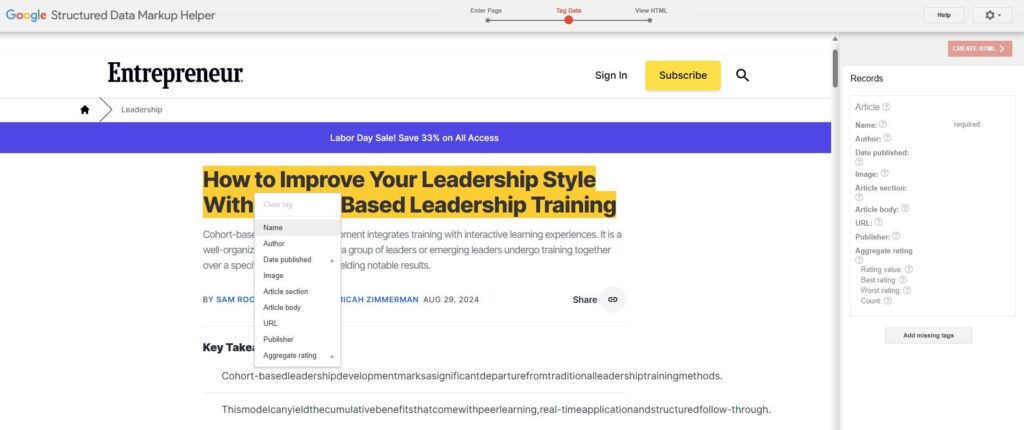
Choose the one that fits, like ‘Name’ for the article title.
Once you tag it, the element will appear in the Records section on the right-hand side of the screen. This list helps you keep track of what’s been tagged.
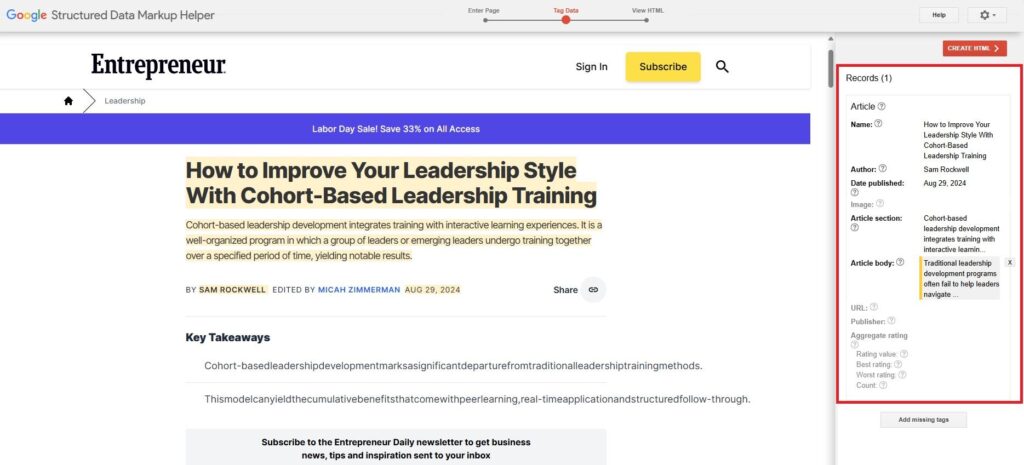
Continue down the page, tagging other important elements like the author, publish date, main content, images, and more. Keep going until you’ve tagged everything you want included in the schema markup.
Step 5: Create the Schema Markup
Once you’ve finished tagging your page elements, click the ‘Create HTML’ button in the top-right corner of the page.
You’ll have the option to generate your structured data in microdata, RDFa, or JSON-LD format.
Choose a format, and the Markup Helper will create the structured data.
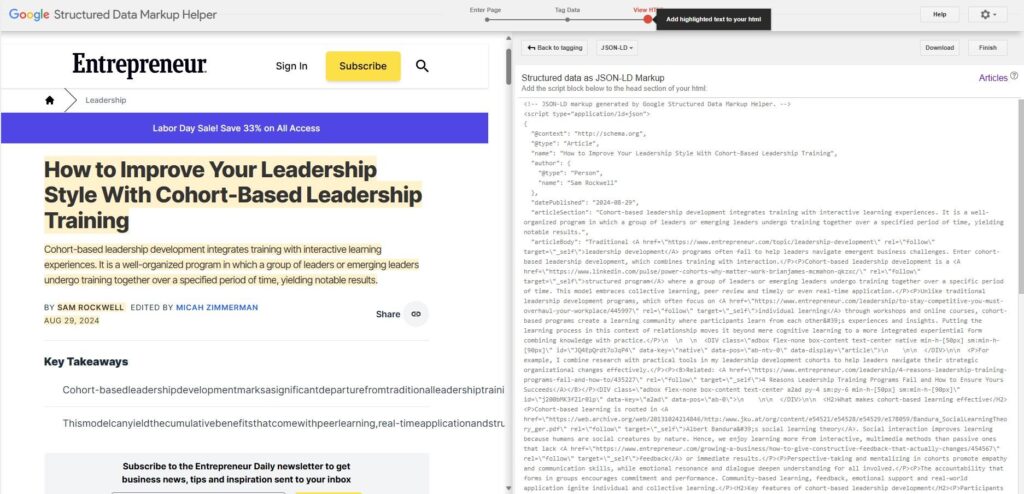
Step 6: Add the Schema Markup to Your Website
Now that your schema markup code is ready, it’s time to add it to your site through your content management system (CMS).
For JSON-LD schema markup, just drop the code snippet into your page header.
If you’re using microdata or RDFa, you’ll need to replace the existing HTML with the new code generated by the Markup Helper.
Step 7: Test Your Schema Markup
The final step is to make sure your schema markup is implemented correctly.
You can use Google’s Rich Results Test to check your page’s HTML.
Just plug in the URL of the page where you applied the markup and run the scan. The tool will show you how many valid pieces of structured data are on the page and flag any errors.
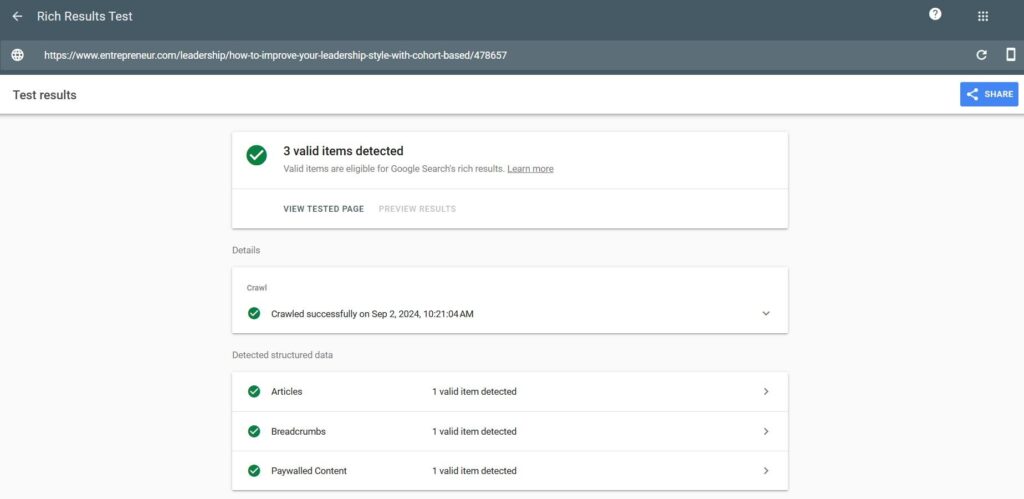
You can also use the tool to see how the rich results will appear to searchers on the SERP.
Boost Search Visibility with Schema Markup
Schema markup is a quick win for your SEO strategy.
You still need great content and solid link building. However, adding schema markup is an easy fix that can make a big difference to SERP visibility and click-through rates.
Focus on your most important pages first, and start grabbing more space and attention on the SERP.
Become a Pro at SEO
Join 65,000 others and learn the secrets to SEO success with our weekly blog posts.
